Retinoblastoma
What Is Retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma is a rare form of eye cancer that primarily affects young children, usually before the age of 5. This cancer develops from the immature cells of the retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It can occur in one or both eyes and if detected early, is highly treatable.
Symptoms of Retinoblastoma:
Common signs and symptoms of retinoblastoma include:
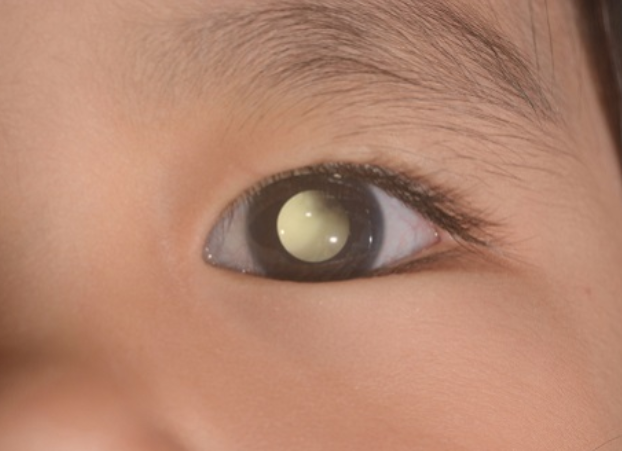
- A white color in the pupil when light is shone in the eye, like when taking a flash photograph (known as “cat’s eye reflex” or leukocoria)
- Redness and swelling of the eye
- A change in the color of the iris
- Poor vision or a decrease in the child’s visual responsiveness
- Crossed eyes or a misalignment of the eyes (strabismus)
Treatment for Retinoblastoma:
Treatment depends on the size and location of the tumor, whether cancer has spread, and the child’s overall health:
- Chemotherapy: To shrink the tumor.
- Laser Therapy or Cryotherapy: To destroy cancerous cells.
- Radiation Therapy: For more advanced cases.
- Surgery: In severe cases, removal of the eye (enucleation) may be necessary to prevent the spread of cancer.
Prevention of Retinoblastoma:
As retinoblastoma is usually caused by a genetic mutation, there’s no known prevention. For families with a history of retinoblastoma, genetic counseling and regular eye exams for children can help in early detection.
To learn more about retinoblastoma, their causes, diagnosis, and surgical options, visit your optometrist.
Please note that this information is provided for informational purposes only and should not substitute professional medical advice. If you suspect you have retinoblastoma or any eye-related concerns, it is important to consult with an eye care professional for a proper evaluation and personalized recommendations.