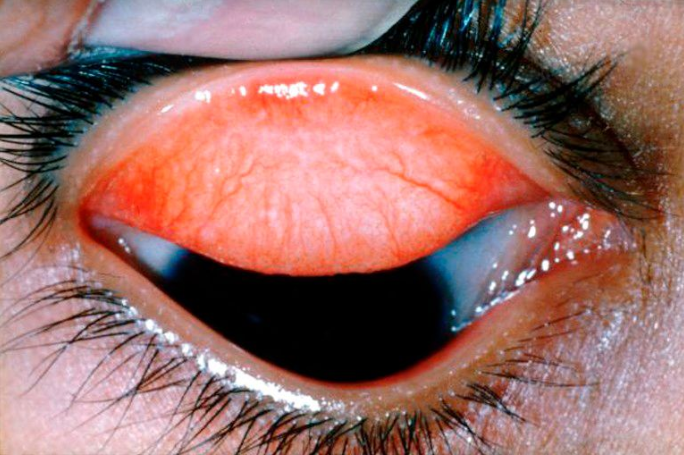
Trachoma
What Is Trachoma?
Trachoma is a contagious bacterial infection of the eye caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is the world’s leading cause of preventable blindness and is most common in poor, rural communities with limited access to clean water and sanitation. Trachoma spreads through direct contact with the eyes, eyelids, and nose or throat secretions of affected individuals, or indirectly via flies that have come into contact with these secretions.
Symptoms of Trachoma:
Early symptoms of trachoma include:
- Mild itching and irritation of the eyes and eyelids
- Discharge from the eyes containing mucus or pus
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
As the condition progresses, it can lead to more severe symptoms and complications, including scarring of the cornea and eyelids, and ultimately, blindness.
Treatment for Trachoma:
Treatment of trachoma aims to eliminate the infection and prevent blindness:
- Antibiotics: The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a single dose of azithromycin, an oral antibiotic, to treat trachoma infection. Topical antibiotics like tetracycline eye ointment can also be used.
- Surgery: For advanced cases, particularly where eyelids are turned inward (trichiasis), surgery may be necessary to prevent the eyelashes from scratching the cornea.
- Improved Hygiene and Sanitation: To reduce transmission, improvements in community hygiene and access to clean water are essential.
Prevention of Trachoma:
Preventive measures are crucial and include:
- Improving community hygiene and sanitation to reduce the spread of the bacterium.
- Regular face and hand washing to reduce transmission.
- Controlling flies in the environment.
- Access to clean water for personal and community hygiene.
Treatments for Cataracts:
The only effective treatment for cataracts is surgery, where the clouded lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Cataract surgery is a safe and commonly performed procedure that can restore clear vision and improve quality of life.
To learn more about trachoma, its causes, diagnosis, and surgical options, visit your optometrist.
Please note that this information is provided for informational purposes only and should not substitute professional medical advice. If you suspect you have trachoma or any eye-related concerns, it is important to consult with an eye care professional for a proper evaluation and personalized recommendations.